Exploring the Differences Between CMYK and CMYK++
In the realm of color printing, achieving the most accurate and vibrant color reproduction is a constant challenge. The traditional CMYK color model, which uses Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black) inks, has been the standard for decades. However, as the demand for more precise and richer color output grows, advancements have led to the development of enhanced printing processes like CMYK++. This article delves into the differences between CMYK and CMYK++, highlighting the benefits and applications of each.
The Traditional CMYK Model
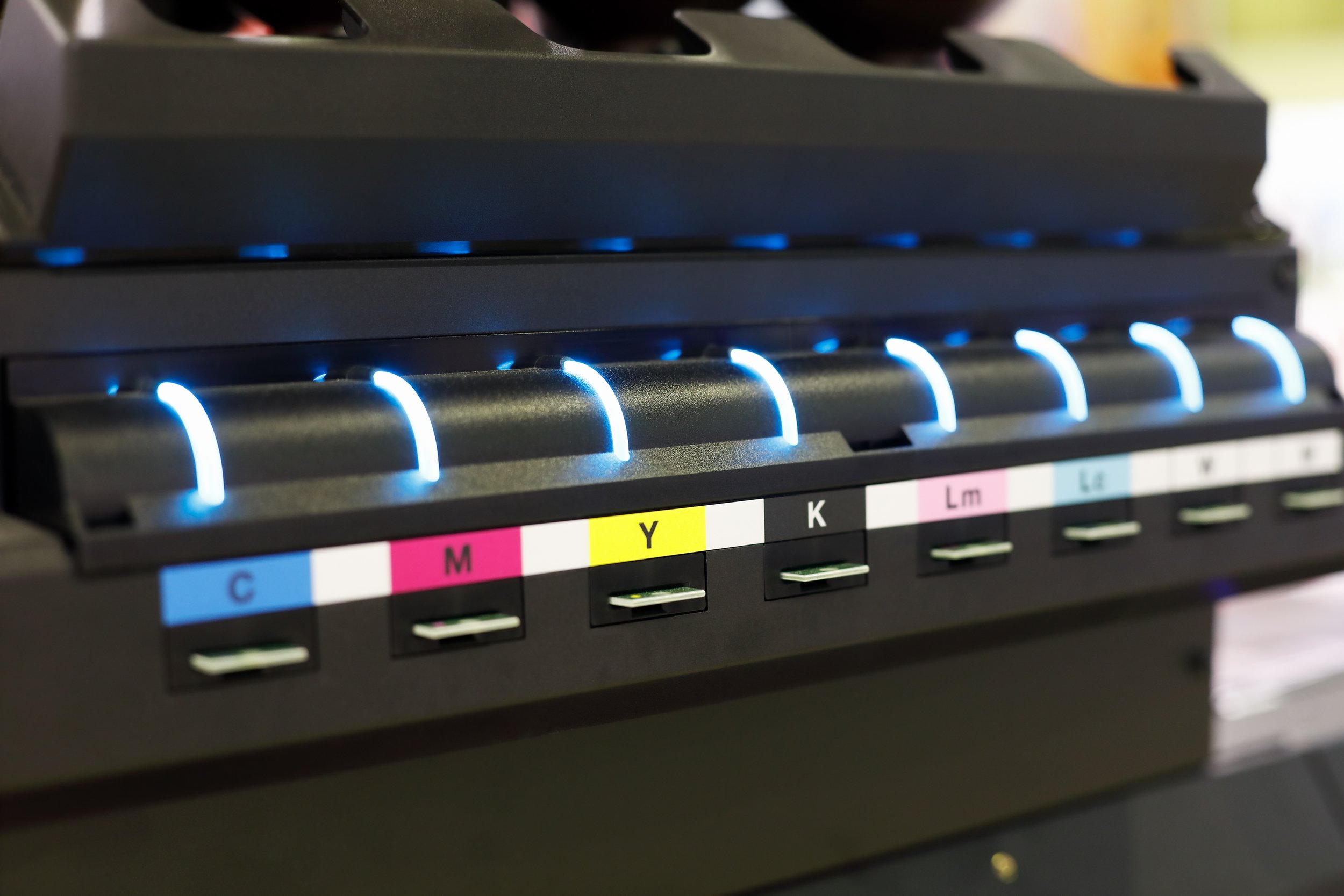
The CMYK color model operates on a subtractive color process, primarily used in color printing. Each color is created by subtracting varying wavelengths of light absorbed by the inks on the white paper. The combination of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks allows for a wide range of colors, but it has its limitations.
CMYK is efficient and cost-effective, making it the industry standard for most printing tasks, from newspapers and brochures to packaging. However, its gamut is relatively limited, meaning it cannot reproduce all colors visible to the human eye. Specifically, vibrant and highly saturated colors, such as bright greens, oranges, and certain blues, are challenging to achieve with CMYK alone.
The Introduction of CMYK++
To overcome the limitations of the traditional CMYK model, the printing industry has introduced CMYK++, also known as expanded gamut printing. This enhanced model incorporates additional inks to the standard CMYK set, such as orange, green, blue, or violet, depending on the specific system used. These additional inks expand the color gamut, enabling the reproduction of more vivid and saturated colors that CMYK cannot achieve on its own.
The most common CMYK++ configurations include:
Hexachrome: Adding orange and green to CMYK.
CMYKOG: Incorporating orange and green inks.
CMYKOGB: Adding orange, green, and blue inks.
Benefits of CMYK++
The primary advantage of CMYK++ over traditional CMYK is the significantly expanded color gamut. This enhancement allows for:
Vibrant Color Reproduction: The additional inks enable printers to produce more vibrant and accurate colors, closely matching the original digital design or photograph.
Consistency and Precision: With a broader gamut, CMYK++ can achieve more consistent color results across different print runs, reducing the discrepancies that often occur with traditional CMYK.
Enhanced Visual Appeal: The ability to reproduce a wider range of colors can make printed materials more visually appealing, which is crucial for marketing and advertising materials where color impact is essential.
Practical Applications
CMYK++ is particularly beneficial in industries where color accuracy and vibrancy are critical. Some of the key applications include:
High-End Marketing Materials: Brochures, flyers, and posters that require eye-catching visuals.
Packaging: Consumer products with packaging that needs to stand out on shelves.
Fine Art Prints: Replicating the rich colors of original artworks.
Photography: Printing photographs with more accurate color reproduction.
Challenges and Considerations
While CMYK++ offers significant benefits, it also comes with certain challenges:
Cost: The addition of extra inks and the need for specialized printing equipment can increase production costs.
Complexity: Managing the color profiles and ensuring accurate color conversion from digital to print can be more complex with CMYK++.
Compatibility: Not all printers support CMYK++, requiring investment in new technology and training.
CMYK++ represents a significant advancement in the printing industry, addressing the limitations of traditional CMYK by expanding the color gamut and enhancing color reproduction. While it involves higher costs and complexity, the benefits of more vibrant, accurate, and visually appealing prints make it an invaluable tool for high-quality printing applications. As technology continues to evolve, CMYK++ is likely to become more accessible, further transforming the possibilities of color printing.